|
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||
The Story Of... Smallpox – and other Deadly Eurasian Germs Much of the credit for European military success in the New World can be handed to the superiority of their weapons, their literary heritage, even the fact they had unique load-bearing mammals, like horses. These factors combined, gave the conquistadors a massive advantage over the sophisticated civilisations of the Aztec and Inca empires. But weapons alone can't account for the breathtaking speed with which the indigenous population of the New World were completely wiped out. Within just a few generations, the continents of the Americas were virtually emptied of their native inhabitants – some academics estimate that approximately 20 million people may have died in the years following the European invasion – up to 95% of the population of the Americas. No medieval force, no matter how bloodthirsty, could have achieved such enormous levels of genocide. Instead, Europeans were aided by a deadly secret weapon they weren't even aware they were carrying: Smallpox.
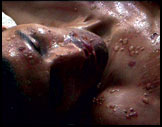
Starting with the hands and the face, and then spreading to cover the rest of the body, each blister is packed full of smallpox DNA. If punctured, these blisters become highly infectious, projecting fresh smallpox particles into the air and onto surrounding surfaces -such as someone else's skin. It is a disease that requires close human contact to replicate and survive. The total incubation period lasts 12 days, at which point the patient will will either have died or survived. But throughout that period, if gone unchecked, they may have passed the disease to an enormous number of people. But the disease requires close human contact to replicate and survive. Smallpox is a remarkably effective, and remarkably stable, infection – research has shown that over the course of 10 years, as few as three individual bases may change in a strain's DNA. The disease found an effective formula thousands of years ago, and there's no reason to change it. So where does this deadly disease come from, and why was it linked to Europeans? For thousands of years, the people of Eurasia lived in close proximity to the largest variety of domesticated mammals in the world – eating, drinking, and breathing in the germs these animals bore. Over time, animal infections crossed species, evolving into new strains which became deadly to man. Diseases like smallpox, influenza and measles were in fact the deadly inheritance of the Eurasian farming tradition – the product of thousands of years spent farming livestock. These epidemic Eurasian diseases flourished in dense communities and tended to explode in sudden, overwhelming spates of infection and death. Transmitted via coughing, sneezing and tactile infection, they wreaked devastation throughout Eurasian history – and in the era before antibiotics, thousands died. But not everyone. With each epidemic eruption, some people survived, acquiring antibodies and immunities which they passed on to the next generation. Over time, the population of Europe gained increased immunity, and the devastating impact of traditional infections decreased. Yet the people of the New World had no history of prior exposure to these germs. They farmed only one large mammal – the llama – and even this was geographically isolated. The llama was never kept indoors, it wasn't milked and only occasionally eaten – so the people of the New World were not troubled by cross-species viral infection. When the Europeans arrived, carrying germs which thrived in dense, semi-urban populations, the indigenous people of the Americas were effectively doomed. They had never experienced smallpox, measles or flu before, and the viruses tore through the continent, killing an estimated 90% of Native Americans. Smallpox is believed to have arrived in the Americas in 1520 on a Spanish ship sailing from Cuba, carried by an infected African slave. As soon as the party landed in Mexico, the infection began its deadly voyage through the continent. Even before the arrival of Pizarro, smallpox had already devastated the Inca Empire, killing the Emperor Huayna Capac and unleashing a bitter civil war that distracted and weakened his successor, Atahuallpa. In the era of global conquest which followed, European colonizers were assisted around the world by the germs which they carried. A 1713 smallpox epidemic in the Cape of Good Hope decimated the South African Khoi San people, rendering them incapable of resisting the process of colonization. European germs also wreaked devastation on the aboriginal communities of Australia and New Zealand. More victims of colonization were killed by Eurasian germs, than by either the gun or the sword, making germs the deadliest agent of conquest. Where to next? Find out more about germs go to the Story of... Malaria. |
|||||||||||
 |
|
| Variables CROPS - Wheat - Rice - Corn - Sorghum ANIMALS - Cattle - Goats - Sheep - Pigs - Llamas - Horse - Zebra GERMS - Smallpox - Malaria TECHNOLOGY - Steel - Writing GEOGRAPHY - Latitude and Climate - Shape of the Continents - Cities and Civilizations |
|